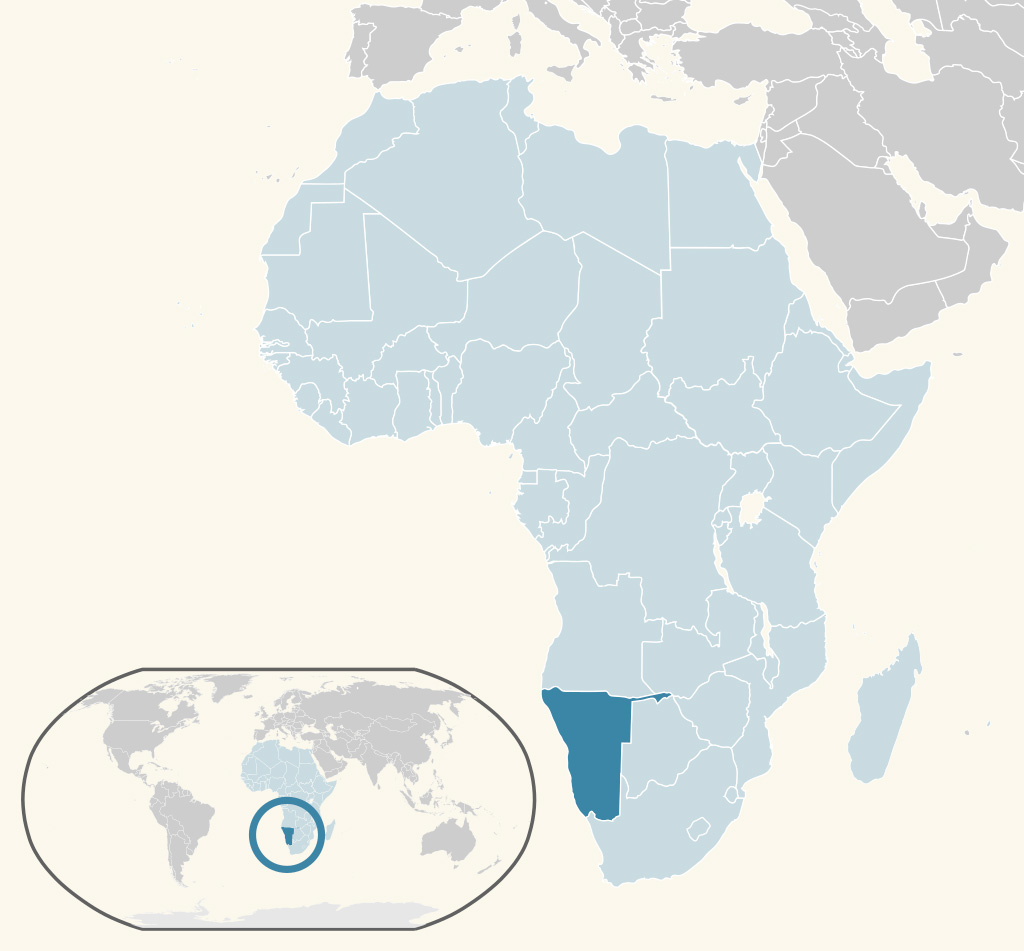
Namibia
Instructions: Read the text. Look at the words in bold.
I was going to talk about India, but at the end I decided to talk about Namibia.
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, and formerly German South-West Africa and then South West Africa, is a country in southern Africa whose western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and east. Although it does not border Zimbabwe, less that 200 metres of the Zambezi River separates them at their closest points. It gained Independence from South Africa on 21 March 1990, following the Namibian War of Independence. Its capital and largest city is Windhoek. Namibia is a member state of the United Nations (UN), the Southern African Development Community (SADC), the African Union (AU), and the Commonwealth of Nations.
Namibia. Retrieved and adapted December, 2016 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Namibia